Learning to play jazz guitar means learning how to tackle the jazz blues form, jazz blues phrases and bringing that bluesy flavor to your improvisations over standard tunes as well. While you may be familiar with how to apply the blues scale and get a blues sound in your rock and blues solos, bringing out the bluesy side of jazz may seem a bit tougher.
In this lesson, you will learn a couple of different ways to bring out a bluesy sound playing over dominant 7th chords. Each of these techniques can be applied to a variety of musical situations.
Lesson Contents
- F Jazz Blues
- Bb Jazz Blues Solo
- Jazz Blues Lick 1 – Mixolydian Mode
- Jazz Blues Lick 2 – Bebop Scale
- Jazz Blues Lick 3 – Mixolydian + Minor Pentatonic Scales
- Jazz Blues Lick 4 – Minor Blues Scale
- Jazz Blues Lick 5 – Minor Blues Scale
- Jazz Blues Lick 6 – Minor Blues Scale
- Jazz Blues Lick 7 – Major Blues Scale
- Jazz Blues Lick 9 – Major Blues Scale (Herb Ellis)
- Jazz Blues Lick 10 – Major Blues Scale (Herb Ellis)
- Wes Montgomery-Style Blues
- F Jazz Blues Chord Solo
- The Minor vs Major Blues Arpeggio Concept
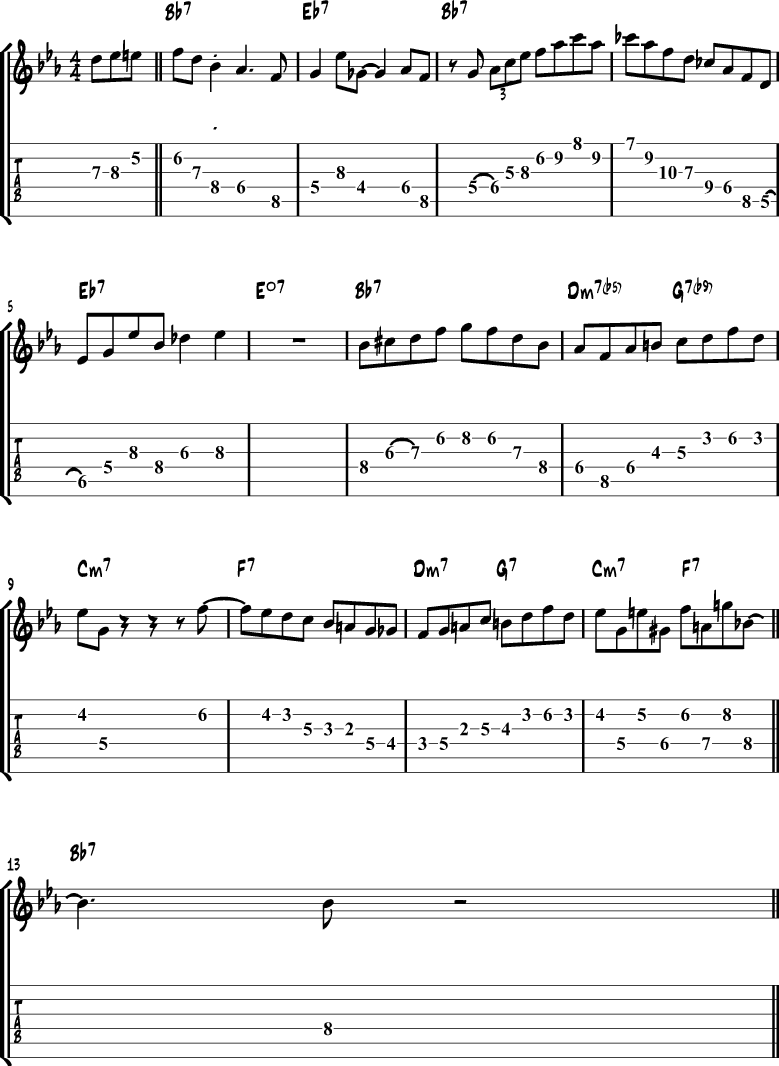
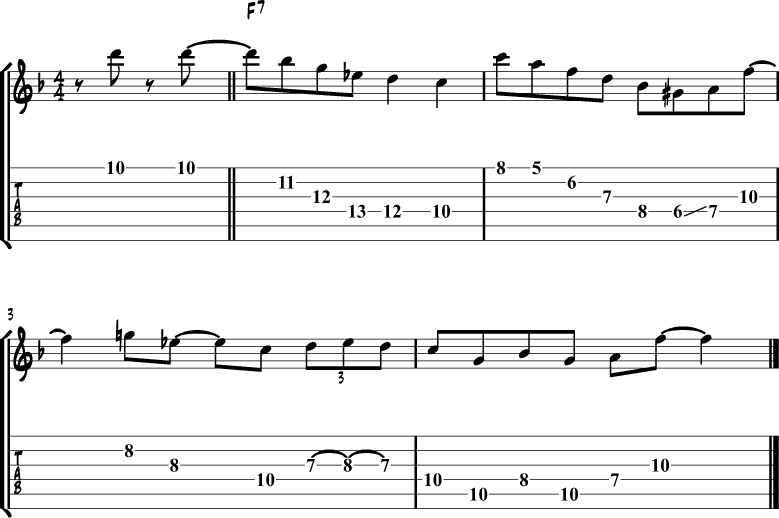
F Jazz Blues
To start this lesson, we’ll have a look at a jazz blues in F, where typical blues riffs are mixed with chord punches.
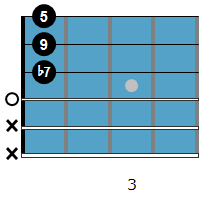
The chord voicing used over the F7 part is an F13.
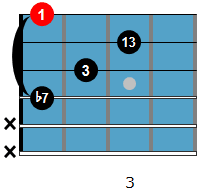
And the voicing for the Bb part is a Bb9.
Backing Track
Listen & Play Along

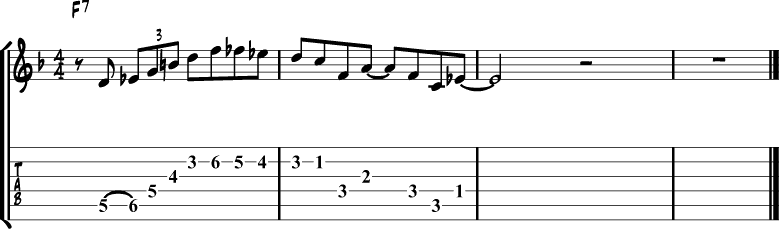
Bb Jazz Blues Solo
Next, we’ll have a look at a typical jazz blues solo over a blues in Bb.
If you’re not familiar with the different types of jazz blues forms, check out our lesson on jazz blues chord progressions.
Backing Track
Listen & Play Along
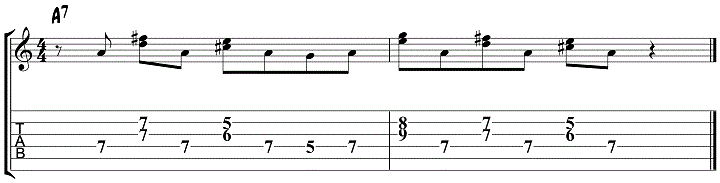
Jazz Blues Lick 1 – Mixolydian Mode
The scales that are used the most in blues are the Mixolydian mode and the minor pentatonic scale, both enhanced with blue notes.
Blue Notes are a drop of pitch of the 3, 5 and 7 of a major scale.
This first phrase is built from the A Mixolydian mode, the mode most associated with the dominant 7th chord sound, and uses double stops on top of an A pedal.
A double stop is a technique where you play 2 notes at once.
This technique, playing double stops on top of a root note, is common practice and is worth exploring further.
Listen & Play Along
Jazz Blues Lick 2 – Bebop Scale
The following lick over F7 uses the F dominant bebop scale, a common choice in jazz to play over dominant chords.
Dominant bebop scale = Mixolydian scale + natural 7
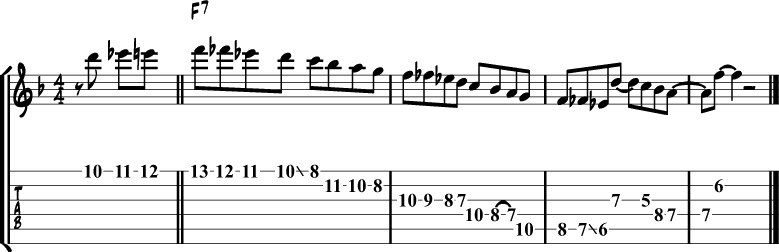
Jazz Blues Lick 3 – Mixolydian + Minor Pentatonic Scales
Most of the blues’ harmony consists of dominant 7th chords. The most popular scale to play over the blues is the minor pentatonic scale.
Why is it that playing a minor scale over a dominant chord sounds so good?
Because the b3 of the pentatonic scale is a blue note to the dominant chord. The tension of the b3 of the scale against the natural 3 of the chord creates the typical blues sound. You can use this tension in your solos by playing with the contrast between the blue note and the natural 3.
Used in rock and blues, the minor pentatonic scale is also a staple of the jazz guitar sound, but used with fewer bends and with a bit of jazz flavor added to it.
Here’s an example lick that mixes two scales.
- The first bar uses the C Mixolydian scale, which has a natural 3.
- The second half of the second bar uses the C minor pentatonic scale, which has a b3.
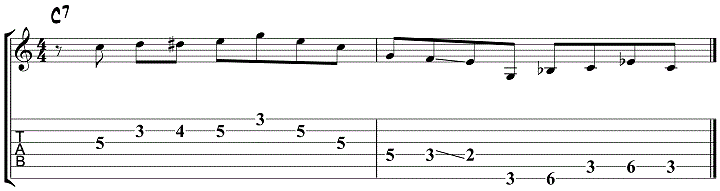
Jazz Blues Lick 4 – Minor Blues Scale
The next example over G7 uses the G minor blues scale.
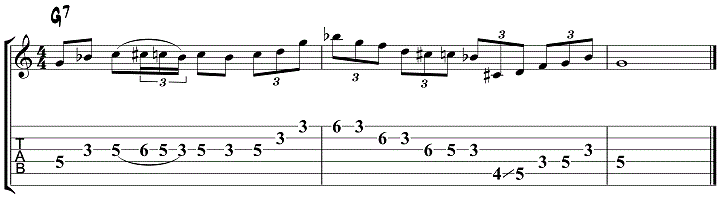
Jazz Blues Lick 5 – Minor Blues Scale
This jazz blues lick uses the A minor blues scale to create an ascending and then descending line over an A7 chord.
Listen & Play Along
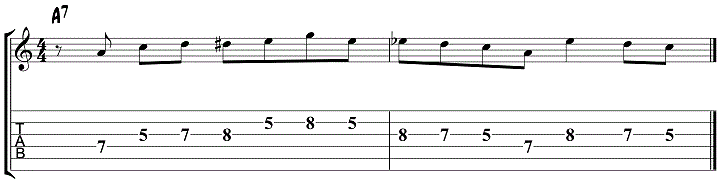
Jazz Blues Lick 6 – Minor Blues Scale
Here’s another example of how to use the minor blues scale, this time over the first 8 bars of the blues progression.
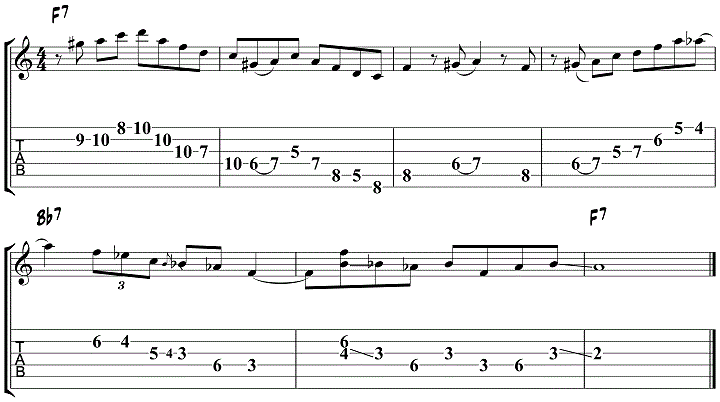
Jazz Blues Lick 7 – Major Blues Scale
We also use the major blues scale to create bluesy phrases.
This lick uses the A major blues scale to create a line over an A7 chord, with the b7 (G) thrown in at the top for good measure.
The first part of this lick is a real blues cliche. Once you know it, you’ll hear it constantly in blues solos (similar to “the lick”).
Notice the slides and slurs in this lick, which can be just as important when getting a jazz sound over the blues as the notes themselves.
Listen & Play Along
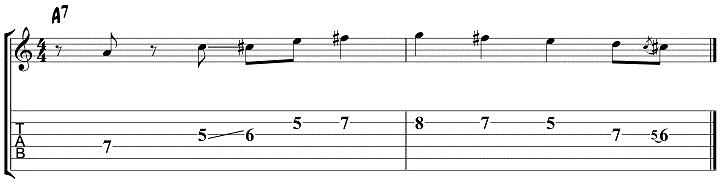
Jazz Blues Lick 8 – Blues Cliche Variation
Here’s a variation of the previous lick, this time in the key of F, and with another cliche added on top.
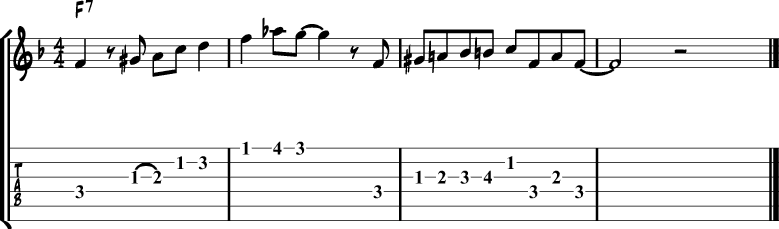
Jazz Blues Lick 9 – Major Blues Scale (Herb Ellis)
Here’s a bluesy lick in the style of Herb Ellis, using the Bb major blues scale.
The 4th measure is in the Bb Mixolydian scale, going to Bb Lydian dominant scale on the 3rd beat.
Jazz Blues Lick 10 – Major Blues Scale (Herb Ellis)
This next lick in the style of Herb Ellis uses the C major blues scale.
Try sliding and/or hammering on the Eb to E each time in order to give this lick that added slipperiness that is characteristic of jazz-blues playing.
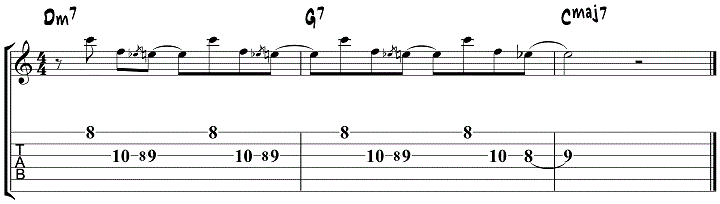
Wes Montgomery-Style Blues
The sound of Wes Montgomery is firmly rooted in the blues. In this section, we’ll have a look at how Wes handles playing over dominant chords.
Jazz Blues Lick 11 – Wes Montgomery Minorization
Wes Montgomery used a concept called minorization to play over dominant chords. Instead of playing a dominant scale or arpeggio over dominant chords, Wes liked to use minor-type arpeggios or scales.
Minorization = playing a minor-type chord built on the 5th or 6th of a dominant chord.
For example: Cm7 and/or Dm7 over F7
| Cm7 Arpeggio | C | Eb | G | Bb |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Played over F7 | 5 | b7 | 9 | 4 |
| Dm7 Arpeggio | D | F | A | C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Played over F7 | 13 | 1 | 3 | 5 |
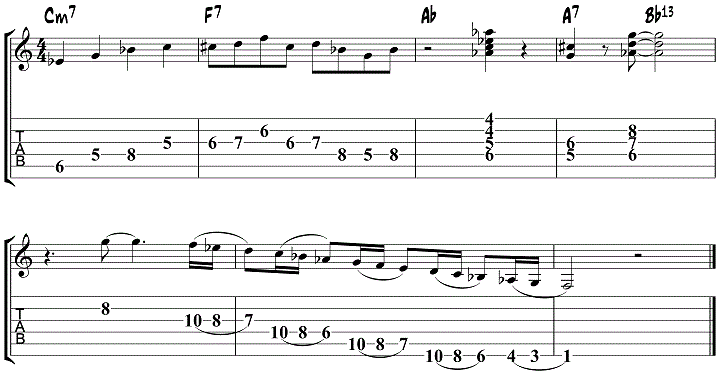
The following lick over F7 is built around C minor.
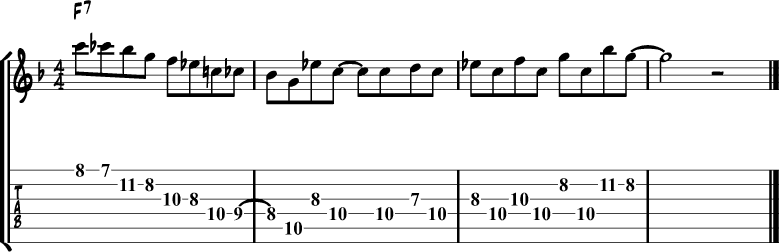
Jazz Blues Lick 12 – C minor over F7
The next lick is also built around C minor.
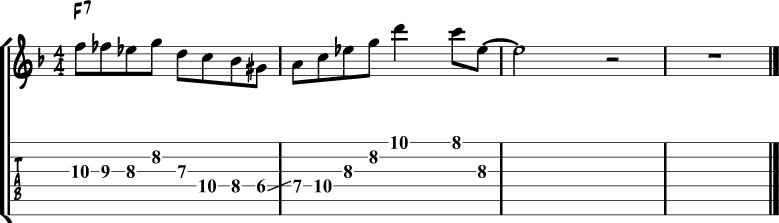
Jazz Blues Lick 13 – Ebmaj7
Another chord substitution Wes Montgomery often used is a major 7 chord built on the b7 of a dominant chord.
For example: Ebmaj7 over F7
| Ebmaj7 Arpeggio | Eb | G | Bb | D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Played over F7 | b7 | 9 | 4 | 13 |

Jazz Blues Lick 14 – Ebmaj7
Here’s another example of that same concept, Ebmaj7 over F7.
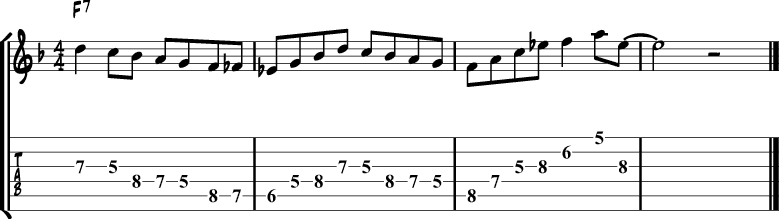
Jazz Blues Lick 15 – Ebmaj7 & Bbmaj7
The next lick starts with an Ebmaj7 arpeggio as well and is followed by a Bbmaj7 arpeggio, before moving to the F Mixolydian scale.
| Bbmaj7 Arpeggio | Bb | D | F | A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Played over F7 | 4 | 13 | 1 | 3 |
Jazz Blues Lick 16 – Eb Augmented Major 7
Another favorite chord substitution of Wes Montgomery is an augmented major 7 chord built on the b7 of a dominant chord.
For example: Ebmaj7#5 over F7
| Ebmaj7#5 Arpeggio | Eb | G | B | D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Played over F7 | b7 | 9 | #11 | 13 |
Wes Montgomery Blues Solo
In this section, you will learn to play a jazz guitar solo in the style of Wes Montgomery.
The solo is over a jazz blues in F and is full of classic Wes licks and ideas that you can apply to your own playing.
Here is the music notation and backing track:

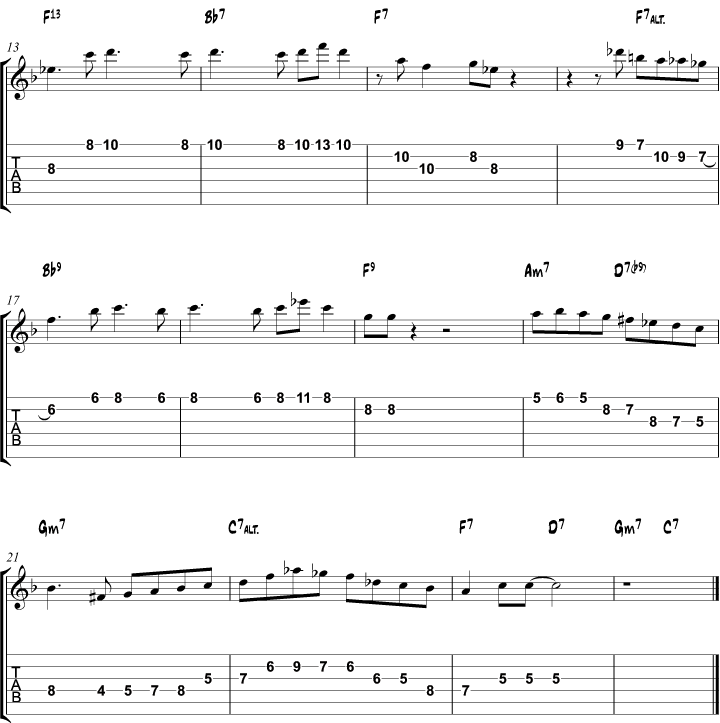
The first 8 bars use the F minor pentatonic scale, mixed with the major 3rd (bar 3).
Mixing b3 and 3 is often used by jazz musicians to create a bluesy sound. One way to do this is mixing the minor blues scale with the Mixolydian scale.
In bar 12, a gm9 arpeggio is used.
You can also use a Bbmaj7 arpeggio to achieve the same sound.
Bar 16 uses the B Lydian Dominant scale (= F altered scale). B7 is the tritone substitute of F7 and creates an altered sound over F.
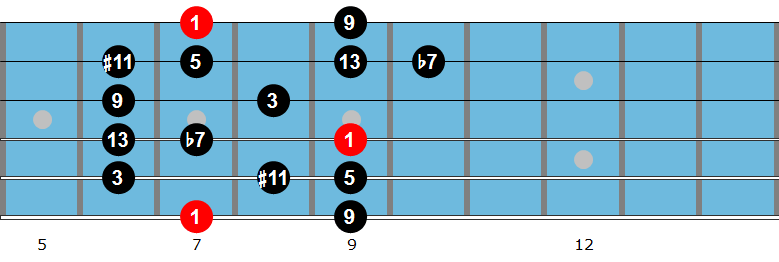
The classic lick in bar 20 uses the G harmonic minor scale over D7, creating a 7b9 sound:
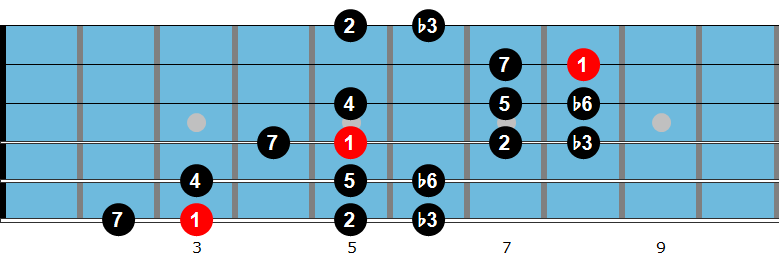
F Jazz Blues Chord Solo
Chord soloing is one of the aspects of jazz guitar that many players want to explore, but often don’t know where to start. Listening to Joe Pass, Barney Kessel, or Lenny Breau tear through a chord solo doesn’t as much inspire as it does intimidate. Because of this, many guitarists avoid studying chord soloing, as they don’t feel ready. Have you been there? I know I have…
This lesson helps you begin your chord soloing studies no matter where you are in your development.
Whether you use this study to expand your chord knowledge or learn to play along with the track, you’ll benefit from this chord solo study.
Check it out, have fun with it, and let it open new doors in your chord soloing vocabulary as you move to the next level in your playing.
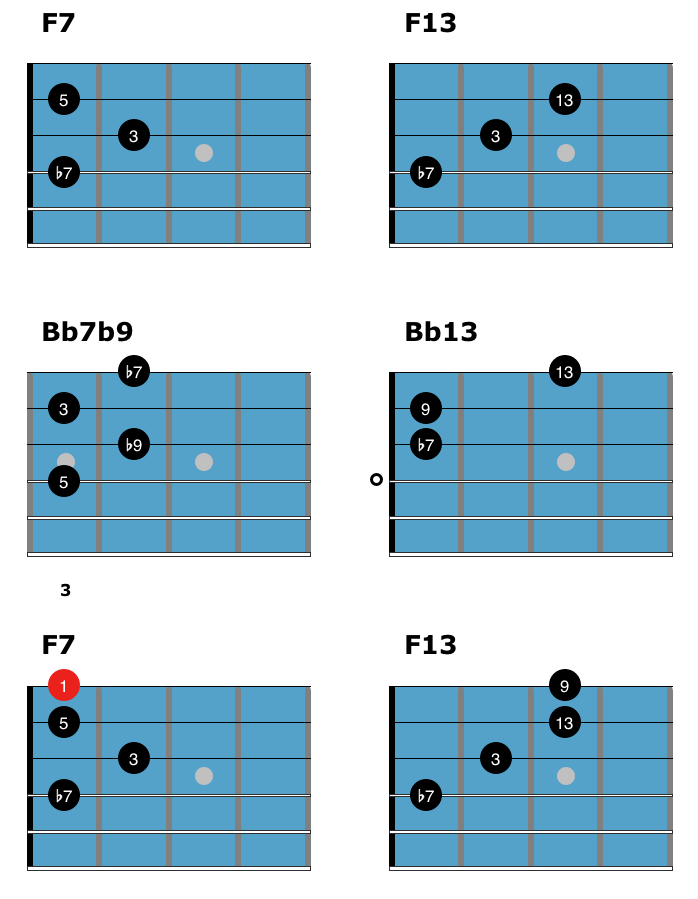
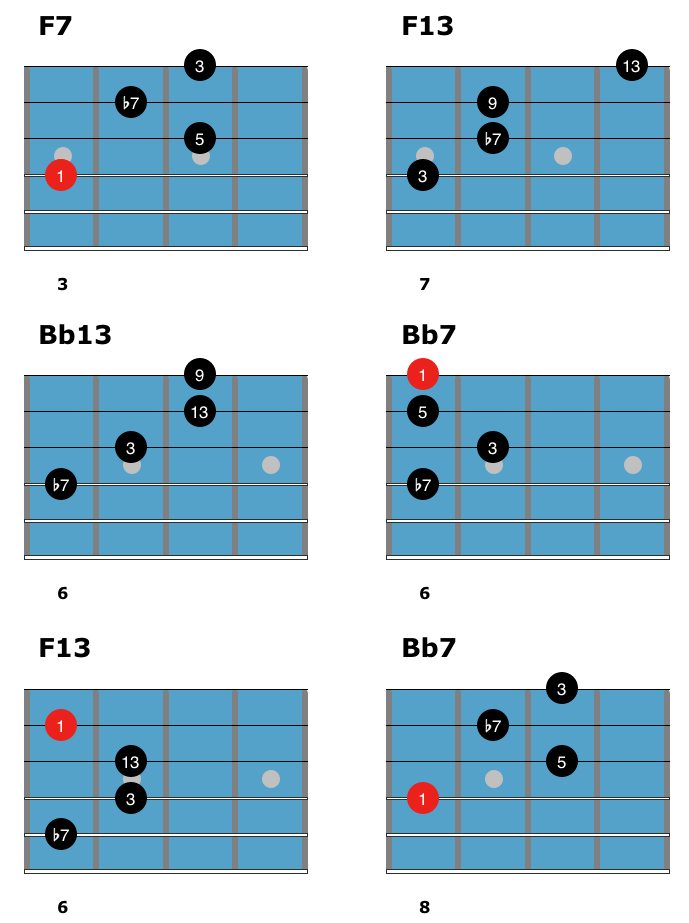
Chords in This Blues Study
Before learning how to play this jazz blues chord solo, here are the shapes used in the study.
Start by playing through each shape to get your fingers used to these chords before you learn them in the study below. You don’t have to memorize these shapes to play the chord solo, but using this page as a reference will be helpful in your comping studies going forward.
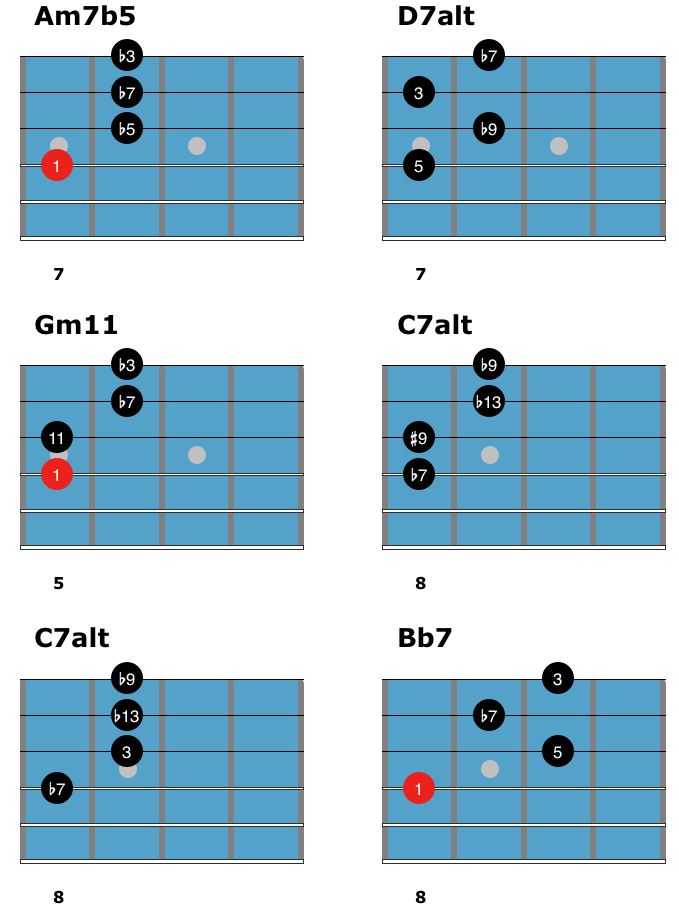
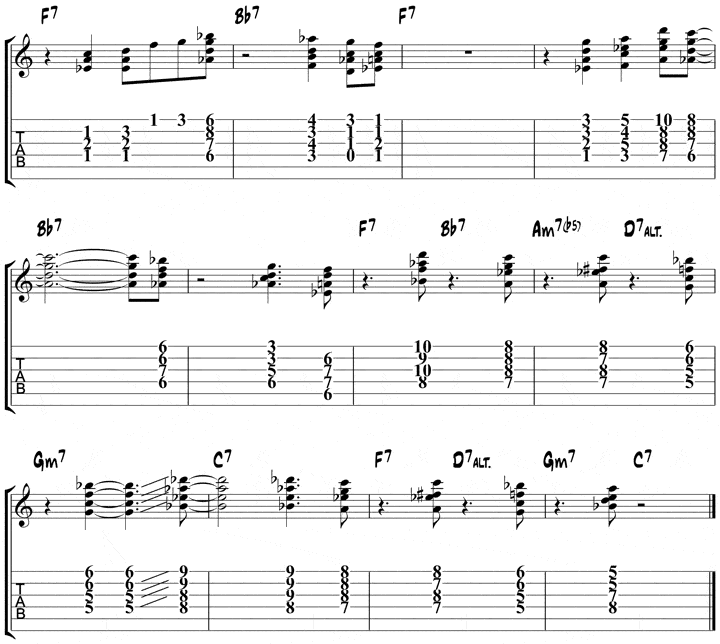
F Blues Chord Solo Study
Now that you know these shapes, you can start learning the chord soloing study.
Start by practicing each four-bar phrase at once, then combine them to play the study as a whole. From there, put on the backing track and jam the study along with the bass and drums on the track.
Backing Track
Listen & Play Along
The Minor vs Major Blues Arpeggio Concept
In this section, we’ll be looking at a simple, yet effective jazz blues soloing concept involving arpeggios that you can use as a gateway into outlining each chord change in a jazz blues progression.
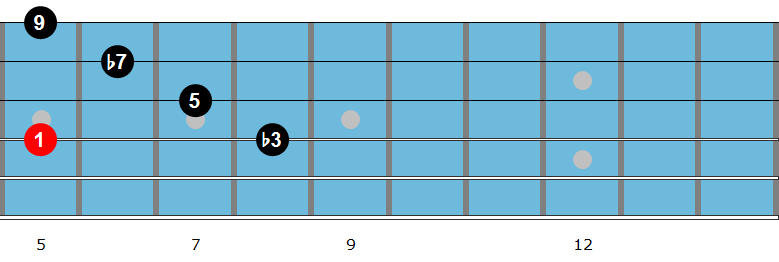
Maj6 Arpeggio
To begin, let’s look at a common fingering for the maj6 arpeggio, which you can then use to outline the I7 chord over any blues progression that you are soloing on.
Here is a Bbmaj6 arpeggio to memorize and begin to solo with, perhaps over a static Bb7 vamp to begin and then over a full blues progression once you have that under your fingers.
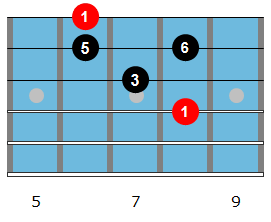
Notice that the notes of this arpeggio (1-3-5-6), when played over a dominant 7th chord highlight the 1, 3, 5 and 13 of that chord. The 6th, when played over a dominant chord, is written and heard as the 13th rather than the 6th. The 13th is just the 6th but raised an octave.
| Bb6 Arpeggio | Bb | D | F | G |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Played over Bb7 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 13 |
Min6 Arpeggio
Now that you have the I7 arpeggio under your fingers, all you are going to do in order to address the IV7 chord in a jazz blues solo is change one note from that initial arpeggio.
By lowering the 3rd of the Bbmaj6 arpeggio you get a Bbm6 arpeggio. You can now apply this new shape to the Eb7 chord (IV7) when soloing over a jazz blues.
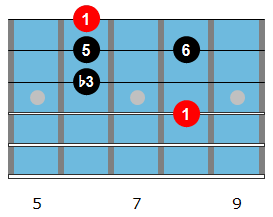
The notes of the Bbm6 arpeggio, when played over Eb7, produces the intervals 5-b7-9-3, giving you a rootless 9th arpeggio to use in your solos over the IV7 chord.
| Bbm6 Arpeggio | Bb | Db | F | G |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Played over Eb7 | 5 | b7 | 9 | 3 |
Now that you have both of these shapes under your fingers, try soloing over a Bb blues progression using the Bb6 arpeggio for the Bb7 chord, and the Bbm6 arpeggio for the Eb7 chord.
Maj6 and Min6 Blues Licks
With the maj6 and m6 arpeggios under your fingers, and a bit of experimentation underway, here are a few sample licks to try out.
In this first lick, you are playing phrase A over the Bb7 chord, then repeating this same phrase over the IV7 chord but with the m6 arpeggio added in.
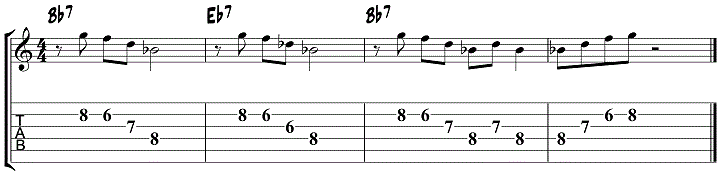
Here you will be adding in the b3 note, considered one of the blue notes, over the I7 chord.
When using the maj6 and m6 jazz blues soloing concept in this way, you can add in notes from the surrounding blues scale in order to spice things up, and break up the arpeggiated nature of the exercise.
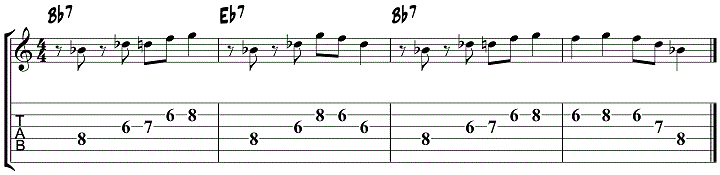
Maj6 and Min6 Blues Solo
To help you get started in applying this jazz guitar soloing concept to a tune, here is a sample solo using simple maj6 and min6 licks to outline the I7 and IV7 chord over a Bb jazz blues progression.
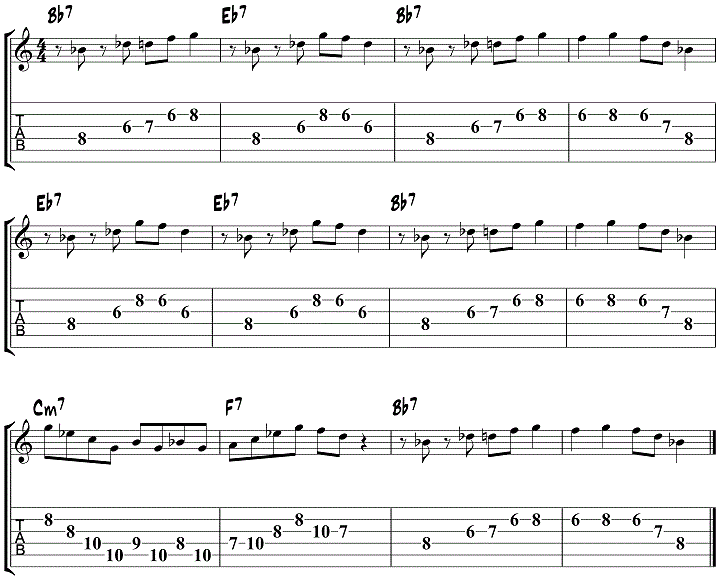
Do you want to learn how to play jazz blues step-by-step? Check out our Introduction to Jazz Blues Guitar Volume 1 and Introduction to Jazz Blues Guitar Volume 2, or buy them both in our bundle below.
The post Jazz Blues Guitar Licks And Solos appeared first on Jazz Guitar Online | Free Jazz Guitar Lessons, Licks, Tips & Tricks..
from Jazz Guitar Online | Free Jazz Guitar Lessons, Licks, Tips & Tricks. https://ift.tt/2qcBQWC


No comments:
Post a Comment