Blue Bossa is a popular bossa nova standard written by Kenny Dorham and made popular by Joe Henderson on his album Page One (1963). It was written after Dorham visited the Rio de Janeiro Jazz Festival in 1961.

Blue Bossa is a good song for beginners to practice improvisation over chord changes because it’s slow and has an easy to follow harmony (including a modulation). Blue Bossa is often played at jams, so it’s a good idea to add it to your repertoire.
Besides The Girl From Ipanema, Blue Bossa must be the most popular bossa nova song ever.
In this lesson, you will learn:
- How to play the melody.
- Which scales you can use to play over Blue Bossa.
- 2 arpeggio studies.
- 2 chord studies.
Blue Bossa Chord Melody
I arranged the melody of Blue Bossa the way you would play it in a jazz trio by adding chords to the melody. When you play in a combo without a piano or another guitar player, it’s a good idea to harmonize your melodies.
I play the theme with a plectrum. The chords I pluck with my plectrum and fingers combined (the plectrum hits the lowest string).
Backing Track
Listen & Play Along
Blue Bossa – Backing Track Video (130 BPM)
To practice improvising over Blue Bossa, you can use the following “Karaoke-style” backing track video, made with Band in a Box.
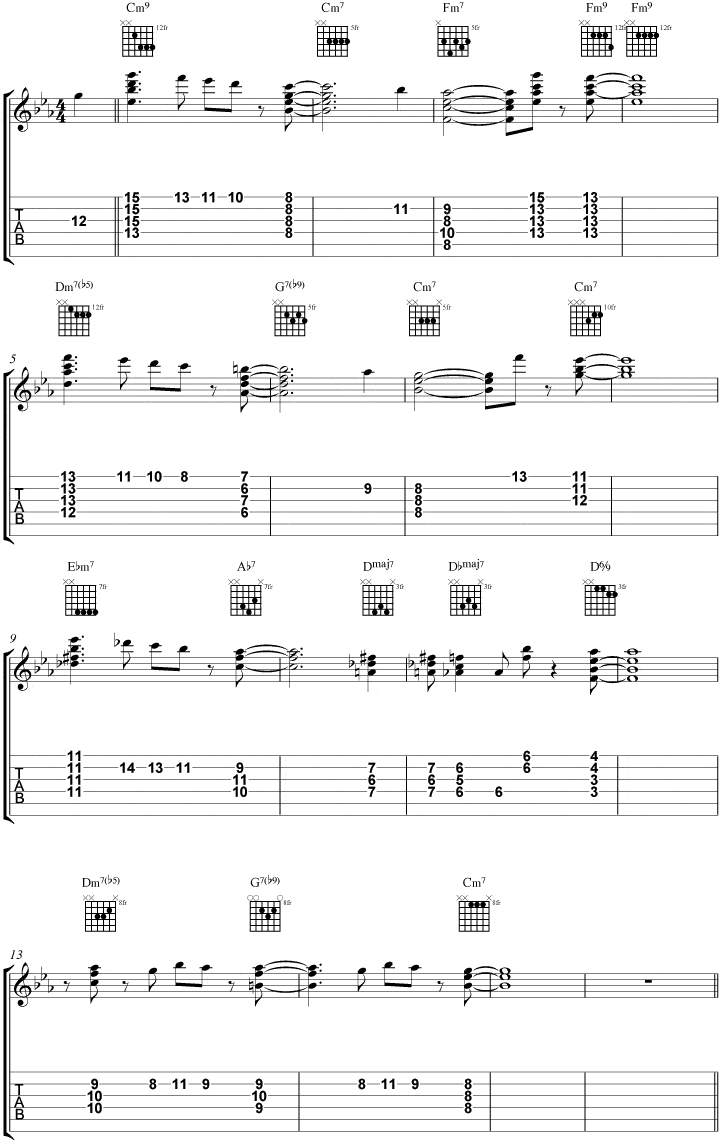
Blue Bossa – Harmonic Analysis
Blue Bossa is a 16-bar tune and is in the key of C minor.
Here are the chords and the scales you can use to solo over the chord changes:
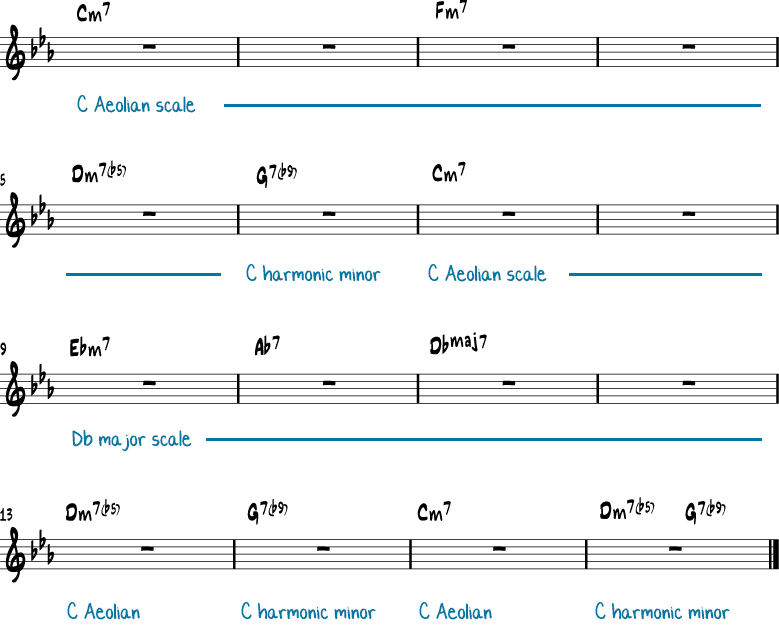
Bars 1-8 and 3-16
On these parts, you use the Aeolian (aka natural minor) scale. The Aeolian scale is one of the guitar modes.
You can also use the C minor pentatonic scale or the C minor blues scale here.
As a variation, you can make bar 2 into a C dominant 7th chord, by playing the F harmonic minor scale.
Bars 6, 14 and 16
On the G7b9, you can use the C harmonic minor scale (=G Phrygian dominant scale) or the G altered scale.
Bars 9-12
Here the chord progression modulates to Db major. It is a regular II V I progression, and you can play the Db major scale (=Db Ionian mode) here.
Blue Bossa – Arpeggio Study 1
Arpeggios are a very important tool for jazz musicians because they enable you to mirror the harmony of a tune in your solo, something that’s harder to achieve with scales.
The best way to learn arpeggios is:
- Memorize the shapes for all chord types in all positions.
- Play them over chord changes in one position without stopping (in continuous 8th notes). This forces you to come out of your comfort zone because you’ll end up in places on the guitar neck that you’re not very familiar with.
- Do this in all positions.
The following arpeggio study over Blue Bossa will help you on your way. I play the arpeggios continuously up and down the strings and stay in one position.
Here’s how you use the study:
- First, memorize the arpeggio shapes of Blue Bossa (see below).
- Play the study a couple of times.
- Now try the exercise without the sheet music. Try starting on another note of the chord. I begin the study on the root of Cm7, but try starting on any other chord tone.
- When you know this position well, go to another position and do the same. Try starting on the C of the 6th string for example.
These studies are not meant to sound good, they sound boring, but they are a good way to master arpeggios so you can use them in a more creative and musical way in your solos.
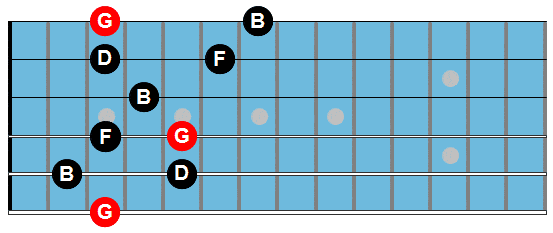
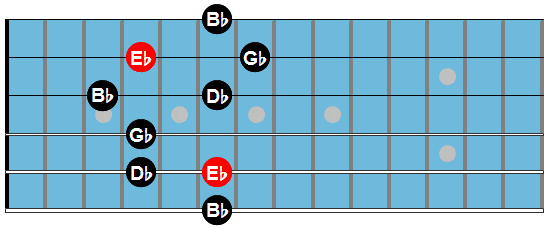
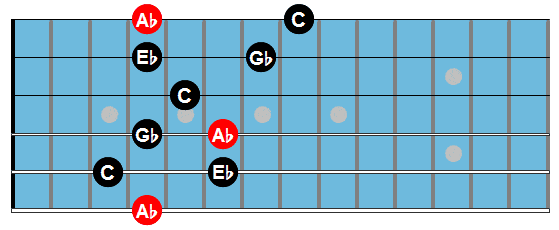
Here are the arpeggio shapes used in this study:
Cm7
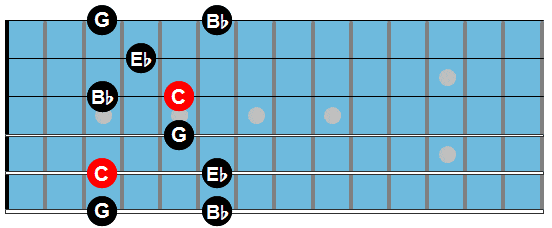
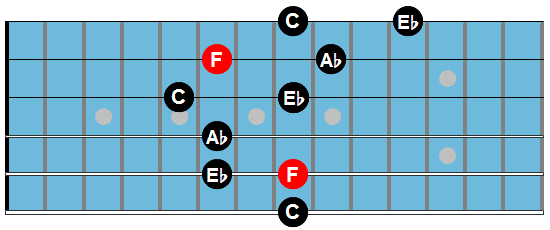
Fm7
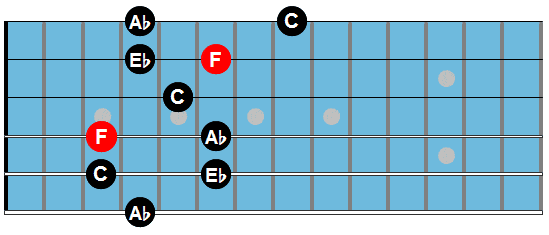
Dm7b5
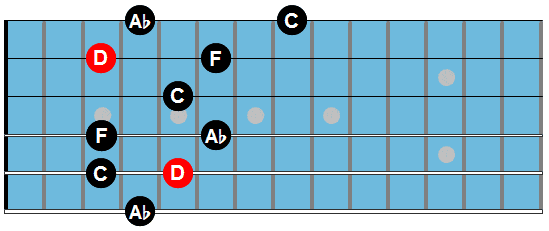
G7
Ebm7
Ab7
Dbmaj7
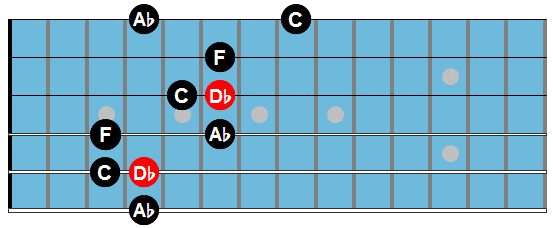
Listen & Play Along

Blue Bossa Arpeggios 2
In study 2 we add the first extension to every chord (the 9) by using chord substitutions.
Here’s how this substitution works:
- You know that chords are built by stacking triads. For example, a Cmaj7 chord consists of these notes: C E G B
- Instead of stopping at the 7, we can add more thirds. In the case of Cmaj7, we can add a third on top of the B, the D.
- The result is a Cmaj9: C E G B D
- Now we omit the root of that chord. These notes are left: E G B D, the notes of Em7.
- Instead of playing a Cmaj7 arpeggio over Cmaj7, we will now play an Em7 arpeggio over Cmaj7.
Playing an Em7 arpeggio over Cmaj7 gives us the major 9 sound:
| Em7 Arpeggio | E | G | B | D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Played over Cmaj7 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 |
Playing substitutions gives us a richer sound compared to playing the vanilla chords, something that is almost always desirable. Make yourself accustomed to playing chord substitutions instead of the plain chords.
Here are the substitutions for Blue Bossa’s chords:
Cm7: Ebmaj7
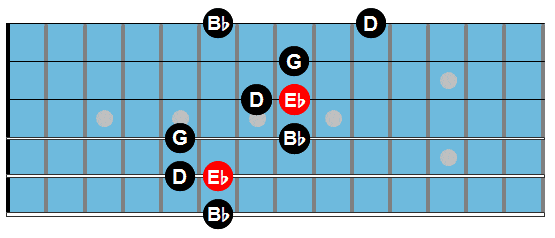
Fm7: Abmaj7
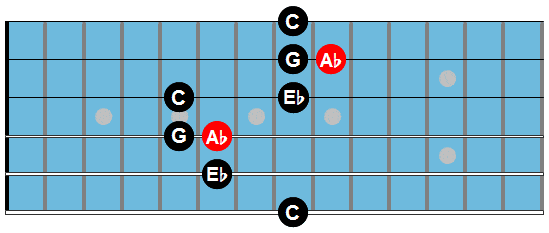
Dm7b5: here we play the plain chord for now.
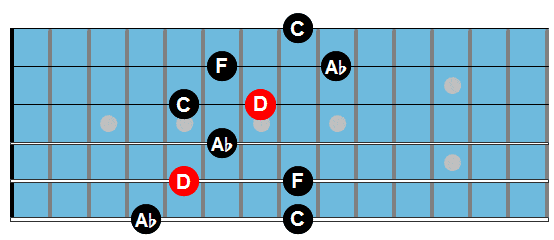
G7: Bdim7
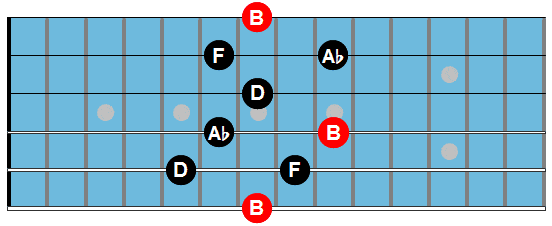
Ebm7: Gbmaj7
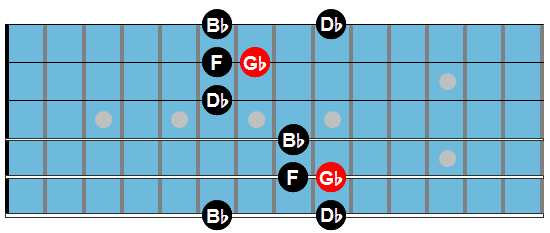
Ab7: Cm7b5
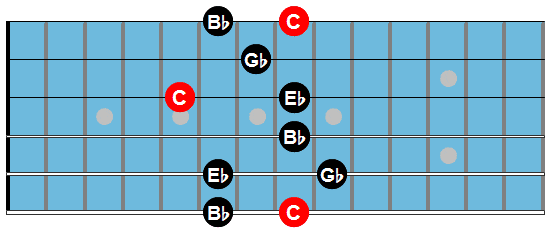
Dbmaj7: Fm7
Listen & Play Along
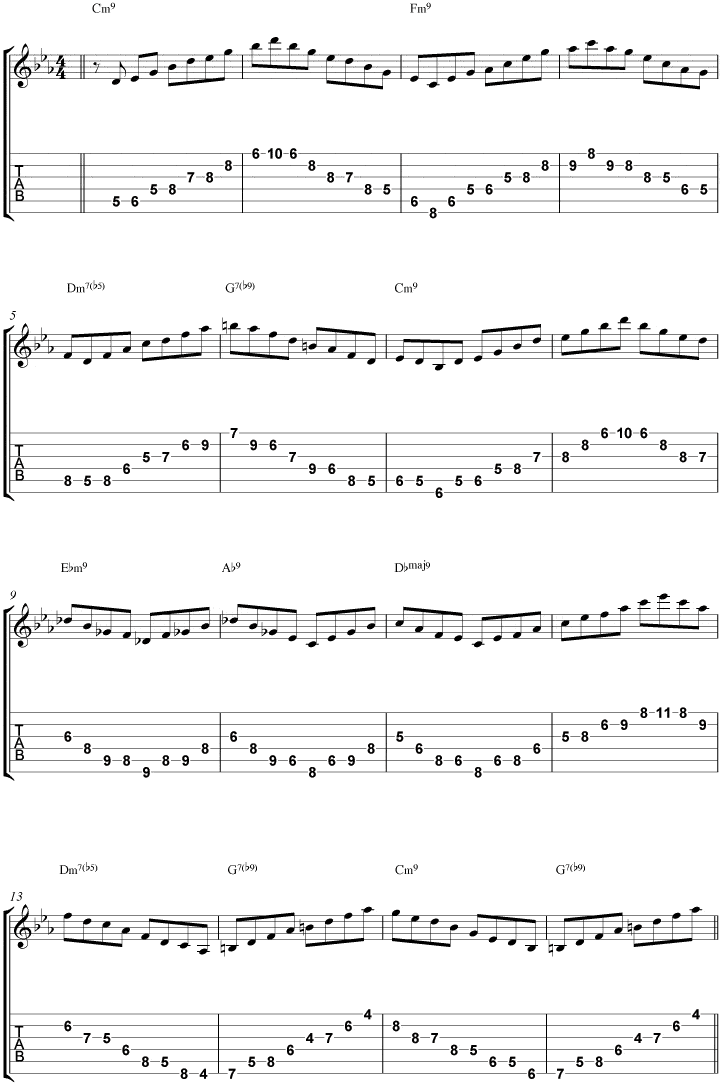
Blue Bossa Guitar Chords
One of the most common non-swing rhythms that jazz guitarists explore when learning how to comp over tunes is the bossa nova groove. While many of us learn to play Brazilian Jazz tunes in our practice routine, learning how to pay an authentic bossa or samba groove on the guitar can be tricky, especially for those players who didn’t grow up in Brazil.
To help you get a handle on how to play an authentic and cool-sounding groove over any Brazilian jazz tune you are learning, we’ve put together a fun to play and engaging chord study featuring a popular Samba/Bossa groove that you can get under your fingers and apply to your playing today.
What’s in These Blue Bossa Chord Studies
You can see in the Blue Bossa chord study below that there is text below many sections of the tune to indicate a certain chord shape or Bossa technique being used at that part of the tune.
To help you understand these concepts further, here are short background descriptions for each of the important chord and Bossa concepts covered in the chord study below so that you can understand the building blocks of this exercise.
m9 Chords – Whereas jazz guitarists prefer m7 chords for minor sounds, it is very common in Brazilian music to use m9 chords instead. These m9 chords, 1-b3-5-b7-9, have a bit of a “softer” sound than m7 chords and help create the smooth sounding quality that we associate with Bossa music.
7b13 Chords – Here, there is a bit of voice leading at play where you are moving from the E note on top of the Dm9 chord for example, to the Eb on top of the G7b13 chord, to the D on top of the Cmaj9 chord. This type of half-step movement on top of chords is commonly found in the playing of many Brazilian guitarists.
Maj9 Chords – Again, this is a softer version of the Maj7 chords that many jazz guitarists prefer to use for their Imaj7 and IVmaj7 chord voicings.
m11b5 Chords – Here, you are replacing the 3rd of Dm7b5 with the 11th in a commonly used alternate shape for a m7b5 chord. When adding this chord into your playing, you can play the m11b5 to the m7b5, or vice-versa, in order to create some melodic movement on top of the chord changes.
Bossa Bassline – During the chord study you will notice that the thumb plays bass notes on 1 and 3 of each bar, mostly the root note but sometimes the 5th or a chromatic note can be added in to create movement as well. When playing these bass notes, you should accent the 3rd beat in order to create a more authentic Brazilian feel with this chord study.
Anticipated Chords – You will notice that between bars one and two, and the first and second bars of each two-bar group, the chord in the second bar is played on the & of 4 in the first bar. This anticipated chord movement is common in Brazilian music, and it will be one of the hardest parts of learning this chord study, or any Brazilian tune on the guitar. So, take your time, isolate these moments and work them on their own before going back and trying to work the study as a whole.
Syncopated Accents – As was the case with the accented 3rd beat in the bass notes, you will want to accent the upbeat chords a little in order to create the swing feel that you hear in Brazilian music. You don’t have to play heavy accents, but just making the upbeats a little louder than the downbeats will help get the authentic Brazilian feel you hear on classic recordings.
Blue Bossa Chord Study 1
In this first Blue Bossa chord study, I play a typical bossa nova rhythm guitar pattern on acoustic guitar.
Notice that bossa nova chord patterns always have the following specifics:
- The bass notes come on the beat and are played with the thumb.
- Usually, the root note is alternated with the 5th (or a b5 in the case of m7b5 chords) in the bass.
- The top voices of the chord are syncopated (syncopation = accenting a normally weak beat).
Listen & Play Along
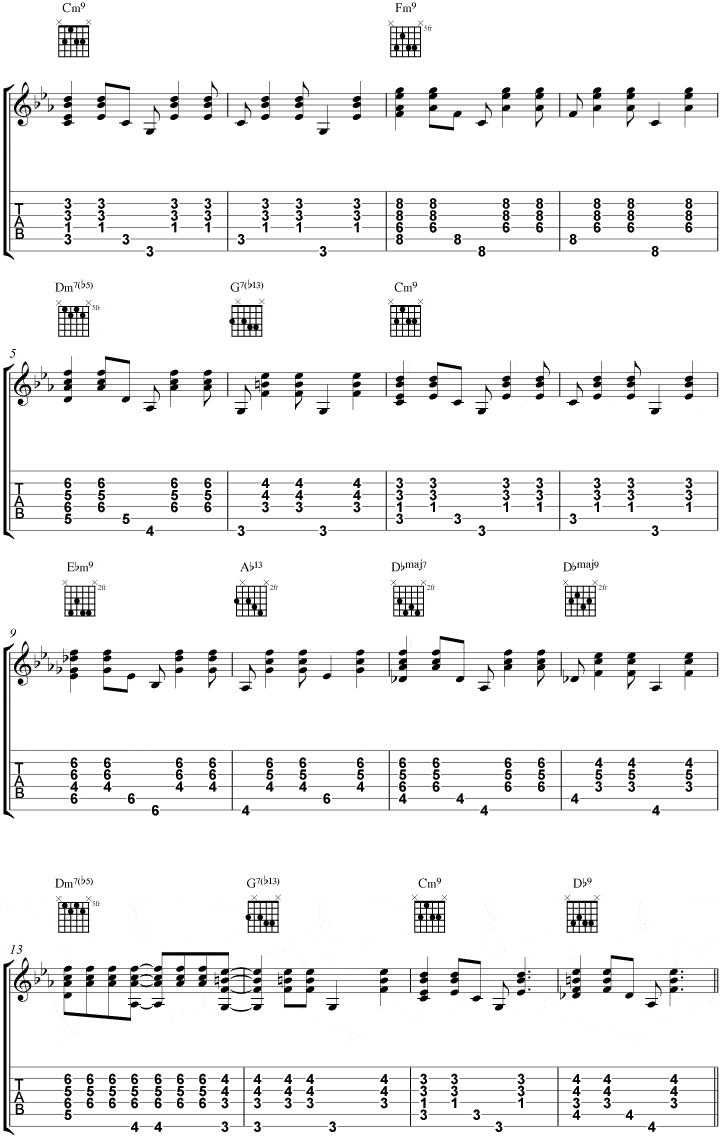
Blue Bossa Chord Study 2
Here is a similar chord study, but this time on electric guitar, without the alternating bass pattern and some variations added in.
The post Blue Bossa appeared first on Jazz Guitar Online | Free Jazz Guitar Lessons, Licks, Tips & Tricks..
from Jazz Guitar Online | Free Jazz Guitar Lessons, Licks, Tips & Tricks. https://ift.tt/2S82wnC


No comments:
Post a Comment